Sleep Now to Live Longer
Sleep is essential to healthy function of our body and mind. Just as your cell phone battery gets depleted and requires a charge every day, so does your body. Sleep enables the body and mind to “unplug” from the stressors of your life and allows for complete relaxation and rebuilding of the body and mind. Healthy sleep also helps the body to fight off disease and recover from he strains you put on yourself during waking hours.
Most adults will require 7-9 hours of sleep each night in order to satisfy their bodies needs. Children and teenagers require substantially more sleep. Dependent on the demands and stress placed on the body, one may require more or less sleep each day.
Much like the tides of the ocean flow in and out, our body too has an internal clock that cycles from the feeling of tired to one of refreshed and alert. This internal clock is referred to as the “circadian rhythm.” After waking in the morning, your energy will slowly be depleted throughout the day, peaking in the evening leading up to your bedtime.
Light affects our circadian rhythm. This is evident as we are naturally more awake when the sun is shining and we begin to tire as the sun sets. In areas of the country where there is very little sunshine, the locals may struggle to find their rhythm, which leads to sleep disturbances. The brain has specialized cells that recognize light and signal to the body that it is day or night.
As the sun begins to set, and natural light diminishes, our body will begin to release melatonin, which causes drowsiness. When the sun rises, our body begins to release a hormone called cortisol that promotes energy and alertness.

Stages of sleep
Our brain will cycle through the following stages throughout the night. There are four stages of sleep. The first three are non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, and the final stage is known as rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
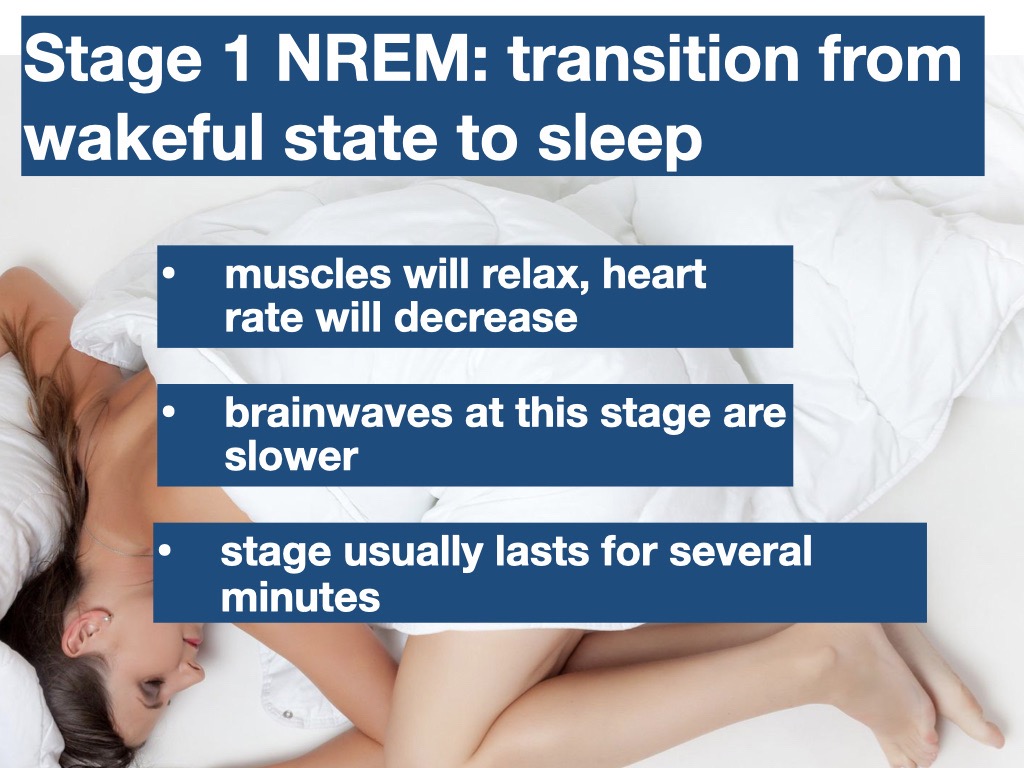
- Stage 1 NREM: The first stage of sleep is where we transition from a wakeful state to sleep. Your muscles will relax, heart rate will decrease, breathing will slow and your eye movements reduce. The brainwaves at this stage are slower and less active than the awake state. This stage usually lasts for several minutes.
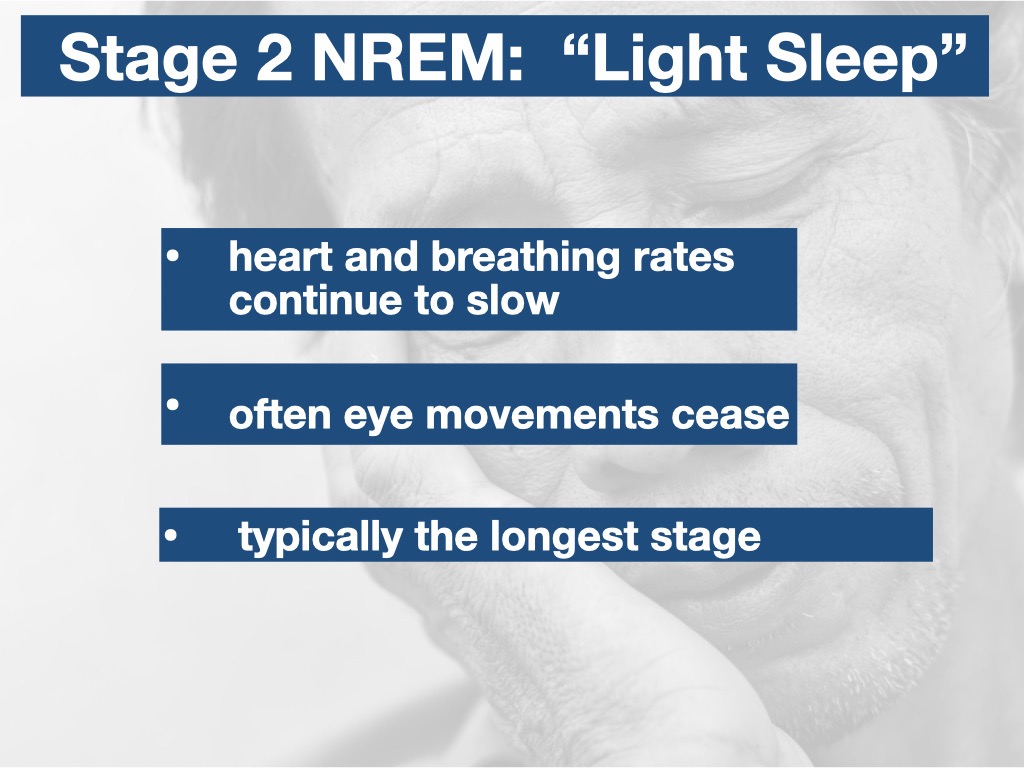
- Stage 2 NREM: “Light Sleep” As your heart and breathing rates continue to slow, your muscles become even more loose and relaxed. At this stage, often eye movements cease and the temperature of the body may decrease. This is typically the longest stage.
- Stage 3 NREM: “Deep Sleep”. This stage is important for making you feel refreshed and alert upon awaking. Heartbeat, breathing and brainwaves are all at their lowest levels. Muscles are as relaxed as they will be.
- Stage 4 REM: The brain will cycle through these 4 stages and the first REM cycle will occur typically after about 90 minutes after you fall asleep. The eyes will dart back and forth under your eyelids. Breathing rate, heart rate, and blood pressure will begin to increase. Dreaming occurs during the REM stage and your arms and legs will be paralyzed during this stage. There have been many studies which link REM to “memory consolidation.” the process of converting short term memories and recently learned experience into long term memory.
- Awake: It should be mentioned that a portion of your time in bed will be spent awake. Sleep disturbances will disrupt the cycles and decrease the time spent in restorative sleep. One might be awake 1-2 hours while in bed.
Therefore, being in bed for 8 hours is not the same as getting 8 hours sleep. Tracking your sleep is the only way you will know with any certainty.In order to feel like you have achieved high quality sleep, your brain must go through each of these stages multiple times per night. The amount of time you spend in stage 3 and 4 will determine the level of restfulness. Sleep disturbances could disrupt the cycle and decrease the needed time in each cycle.
Most people undervalue the need for sleep and drink coffee or other stimulants to help them stay awake throughout the day. They may say, “I’ll sleep when I’m dead,” or “I don’t have time for sleep.”
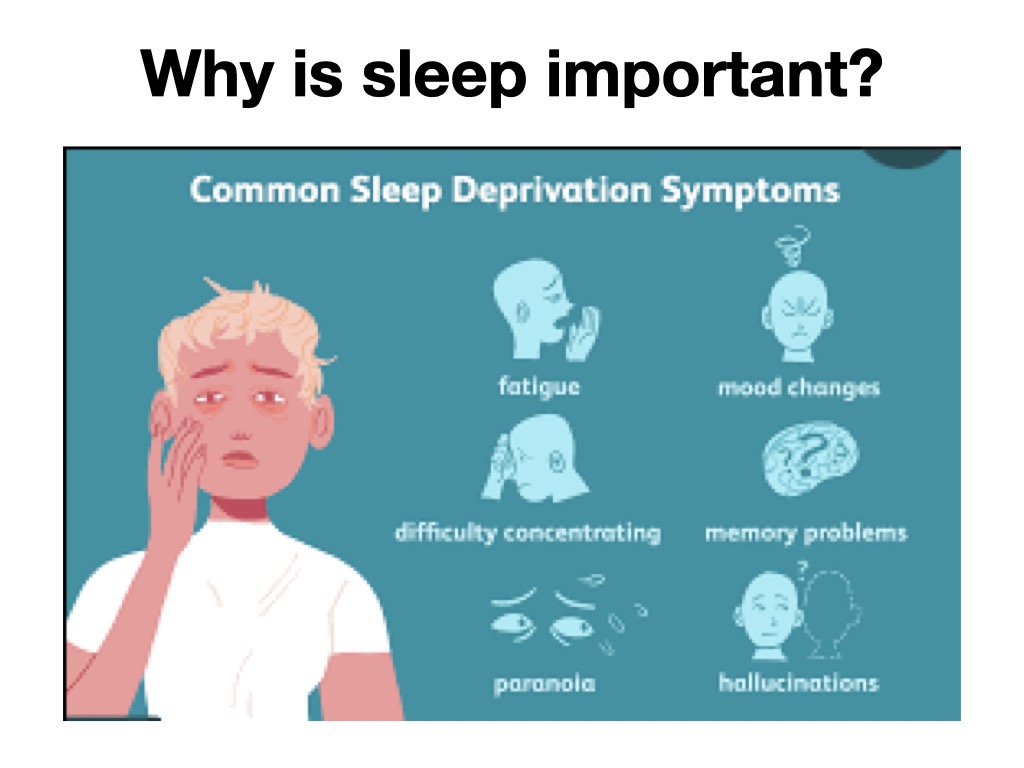
Lack of sleep will leave you dragging, fatigued, forgetful and cranky. When you feel like this, you are much less likely to be motivated and inspired to live your best life. In fact, you may choose to reduce your activities, avoid people, restrict your engagements and reduce your activities.
When chronically sleep deprived, this will have a significant impact over longer time periods. Sleep deprivation will lead to decrease performance of our minds and bodies. Sleep influences the immune system, memory consolidation, attention, hunger, moods, response time, and many other bodily functions.
Sleep deprivation may be very obvious after a long night with little sleep. However, its affects are not so obvious when we are deprived every night. We may actually start to believe that feeling run down and tired is normal and all we need is more coffee or stimulants to keep going.
This false thought leads us to covering up the side effects and accepting the negative impact sleep deprivation has on our life and those we spend time with.
For children, sleep is essential for the proper growth and development. When kids are tired it impacts their ability to perform in school. Their memory is also negatively affected which limits their potential.

When you’re tired and run down it appears to affect the immune system. You are more susceptible to illness and have a decreased capacity to fight infection.
Chronic sleep deprivation also affects your mood, behavior and emotional health. It alters brain function in certain regions of the brain. It may be more difficult to control emotional outbursts when you are tired.
The National Heart Lung and Blood Institute states that people who suffer from sleep deficiency are more likely to develop high blood pressure, diabetes and heart disease.

How do you improve your sleep?
- Track your sleep patterns with technology. There are many devices to help you track your sleep to help get on the right path. ie. Whoop, Oura Ring
- Develop healthy sleep patterns by going to sleep and waking up at consistent times.
- Get sun exposure for 20-30 minutes per day
- Decrease your intake of stimulants
- Decrease or eliminate alcohol.
- Get 8 hours of sleep per night.
- Lower the temperature in the room. Lower temperatures encourage sleep.
- Decrease or eliminate screen time prior to bed
- Create a sleep pattern or habit that you can do each night which prepares your mind and body for relaxing and sleep. ie. brush teeth, wash face, meditate, read, gratitude journal
- Ensure that you are exerting and depleting your energy during the day so you will be tired at bed time. Exercise, run, walk, play….do something to use your energy.
Harvard Medical School. Characteristics of Sleep. http://healthysleep.med.harvard.edu/healthy/science/what/characteristics Retrieved December 2016.
National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Why is Sleep Important? https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/sdd/why Retrieved December 2016.